Hypochlorite topic|Acidic electrolytic water gives mold nowhere to hide!
Hypochlorite topic|Acidic electrolytic water gives mold nowhere to hide!

Mold as a common class of microorganisms in life, is the formation of branched mycelium fungi collectively, they can often form a branched mycelium, but not like mushrooms to produce large substrates. Mold like temperature and humidity, in a warm and humid environment are able to grow and reproduce, so food, feed, furniture, clothing, and even walls, floors in the wet season are very susceptible to mold.

Among them, some mold in the process of growth and reproduction will produce a class of toxic secondary metabolites, called mycotoxins. These mycotoxins through food, feed, etc. into the human and animal body, causing acute or chronic toxicity in humans and animals, damage to the body’s liver, kidneys, neural tissue, hematopoietic tissue and skin tissue, thereby threatening the life of the organism. At present, there are about 150 species of mold can produce toxins, the mycotoxins produced by more than 300 species, of which the most famous is the “number one killer” aflatoxin.
As mold and mycotoxins to human and animal health has brought a huge threat, so people for the prevention and treatment of mold has never slowed down. In recent years, numerous scientific studies have confirmed that acidic electrolytic water treatment has a significant effect on the prevention and treatment of mold in food and living environment.
The effect of micro-acidic electrolytic water on the control of black mold
The research group of Angelica Naka at the University of Tokyo, Japan, evaluated the effectiveness of micro-acidic electrolytic water on the removal of molds formed in the home environment by using 40mg/L of micro-acidic electrolytic water for cleaning. Therefore, in this study, the black mold produced in the household grid board was used as the experimental object and cleaned with 40mg/L micro-acidic electrolytic water, and the black mold was completely removed after 5 times of continuous cleaning, and the effect was significantly better than that of ordinary tap water. This study shows that the micro-acidic electrolytic water is very suitable for disinfection of objects in the home.

The effect of micro-acidic electrolytic water on the control of Staphylococcus griseus
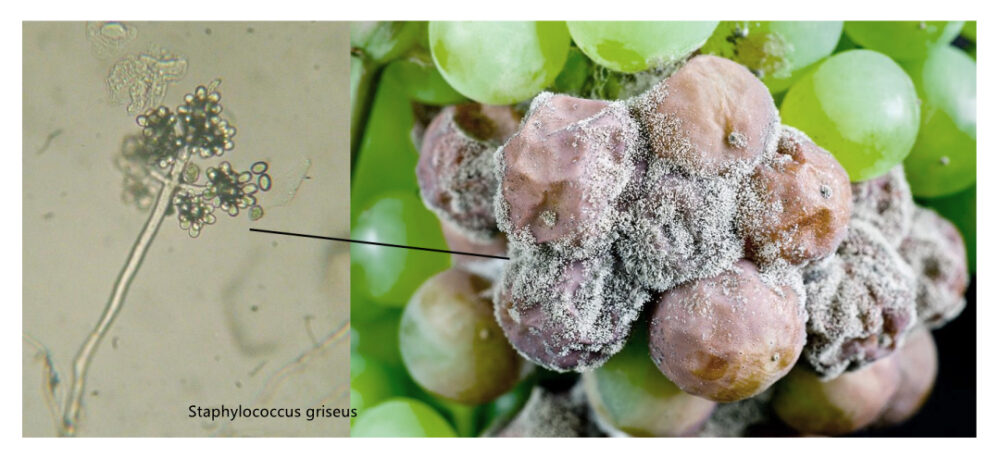

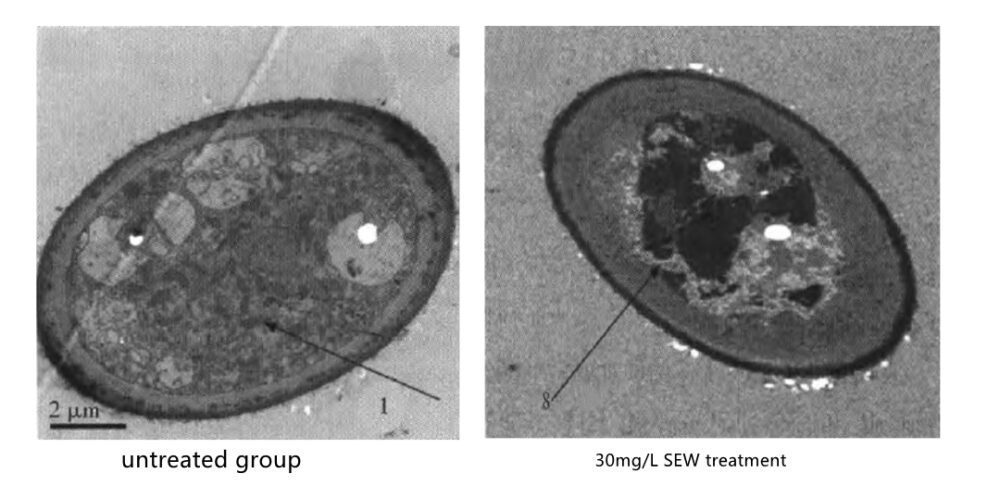
Professor Zhu Songming’s team from Zhejiang University has conducted a study on Staphylococcus griseus (one of the common plant molds) and found that the inactivation rate of Staphylococcus griseus reached 99.99% after 10min treatment with 30mg/L micro-acidic electrolytic water; after treating the formed Staphylococcus griseus colonies continuously for 3 days, it could kill the newborn spores of Staphylococcus griseus and inhibit its mycelial growth, during which the mycelia The colonies gradually turned dark yellow and wilted until they died, and the colonies stopped growing.
The killing mechanism was investigated by scanning transmission electron microscopy, and it was found that the treatment with micro-acidic electrolytic water caused the spore cells of S. cerevisiae to undergo wall separation, cytoplasmic overflow, organelle dissolution and cell crumpling, thus inactivating them and killing them completely.
Effect of micro-acidic electrolytic water on the control of Aspergillus griseus
Effect of micro-acidic electrolytic water on the control of Aspergillus griseus
Professor Li Ritter’s team from China Agricultural University has conducted a series of studies on Aspergillus flavus and found that micro-acidic electrolytic water can destroy the cell structure of Aspergillus flavus conidia and mycelium, resulting in intracellular K+ and Mg2+ leakage, which in turn has a strong killing and inhibiting effect on Aspergillus flavus conidia and mycelium; in addition, the use of micro-acidic electrolytic water soaking can also effectively degrade aflatoxin B (AFB1) in naturally contaminated peanuts, with a degradation rate of 85%. AFB1), with a degradation rate of 85%.
Taken together, micro-acidic electrolytic water has good application effect and potential in mold control, which not only has significant killing and inhibiting effect on most molds, but also can reduce mycotoxin content and effectively control the risk of mycotoxin threat to human body, thus enhancing people’s life safety quality.
References.
[1] Kurahashi, M. . (2021). Slightly acidic electrolyzed water to remove methylobacterium mesophilicum, rhodotorula mucilaginosa and cladosporium cladosporioides in households. Applied Microbiology, 1.
[2] Nan Songjian, Huang Xiaoling, Wang Shuo, Ye Zhangying, & Zhu Songming. (2019). Study on the fungicidal effect and mechanism of action of micro-acidic electrolytic water on Staphylococcus griseus. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 50(1), 6.
[3] Xiong Ke, Li Xiuting, Liu Haijie, & Li Ritter. (2014). Study on the removal of aflatoxin b_1 by acidic oxidative electrolytic water. Chinese Journal of Food Science (8), 9.



